PSORIATIC
ARTHRITIS The hallmark of psoriatic arthritis is a combination of productive
and aggressive erosive changes with severe joint space narrowing. Normal materialization
is maintained.
1. Distribution:
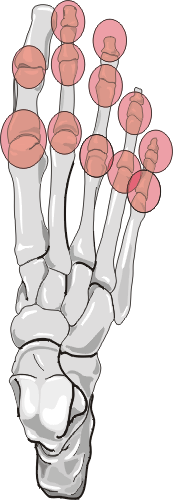
There is asymmetric bilateral distribution, primarily involving hands. In
addition, feet, SI joints, and spine are involved in decreasing order of frequency.
There are three patterns of involvement of psoriatic arthritis in the feet.
First pattern primarily involves DIP, PIP, and MTP. Second pattern is single
ray involvement where all the joints of one digit are involved while other
fingers are spared. The third pattern is similar to rheumatoid arthritis distribution.
Fusiform soft tissue swelling involving a single ray can occur giving the
appearance of 'sausage digit'.
2. Erosion
pattern:
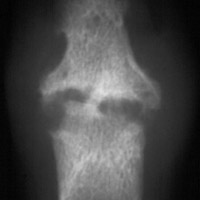
Erosions appear peripherally and progress to involve central area.
Erosions are described as having fuzzy margins. 'Pencil-in-cup' deformity
occurs when distal head of a bone becomes pointed appearing as if it had been
sharpened and the adjacent articulating surface becomes 'saucerized' through
erosions. Resorption of terminal tufts may also occur. In the feet, erosions
with fuzzy margins and bony proliferation may be observed along the posterior
and inferior aspect of the calcaneus at the attachment of Achilles tendon
and plantar aponeurosis. Bone proliferation may occur adjacent to erosions,
along shafts, across joints, and at tendinous or ligamentous insertion. Bone
proliferation along the shaft is observed as periostitis, usually described
as fluffy. Bone proliferation around distal phalanx of the great toe leads
to 'ivory phalanx" appearance. Bone production adjacent to erosions leads
to appearance of "mouse ears" .
3. Differential diagnosis:
The presence
of bone proliferation and bony ankylosis, and the lack of osteoporosis are common
finding of all seronegative arthritis and are useful in the differentiation
of psoriatic arthritis from rheumatoid arthritis. The distinction among seronegative
arthritis is based on the distribution, psoriatic
arthritis involves hands and feet, Reiter's has a predilection for the lower
extremity, while ankylosing spondylitis
has a predilection for the axial skeleton with only rare involvement of the
small joints of the appendicular skeleton.