Ankylosing
spondylitis (AS) is a HLA-B27 spondyloarthropathies which is characterized
by bony ankylosis and syndesmophyte formation.
Distribution:
It primarily affects the axial skeleton and secondarily the appendicular skeleton
to involve proximal large joints in a bilateral symmetrical distribution.
The arthropathy begins in the SI joints and then progresses to the lumbar
spine and ascends to involve the thoracic and cervical spine. Afterwards,
arthritis progresses to involve the hips, shoulders, knees, hands, and feet
in decreasing order of frequency. In early stages, bilateral symmetric erosions
involving the SI joints are present which is followed by sclerosis which eventually
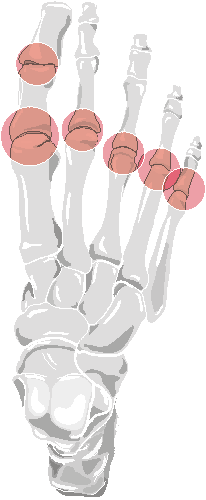
results in bilateral ankylosis. The feet are affected in about 10% of patients
in later stages of the disease. The IPs and MTPs are affected.
Erosion pattern:
Erosions are usually superficial, with productive response. Intra-articular
ankylosis occurs in a short period of time.
3. Differential
diagnosis:
The presence of bone proliferation and bony ankylosis, and
the lack of osteoporosis are common finding of all seronegative arthritis and
are useful in the differentiation of ankylosing spondylitis from rheumatoid
arthritis. The distinction among seronegative arthritis is based on the distribution,
ankylosing spondylitis
has a predilection for the axial skeleton with rare involvement of the small
joints of the appendicular skeleton.