Dislocation
Incidence:
- 1-3% for primary total hip arthroplasties (Ali
Khan, Lewinnek)
- 16% for revision arthroplasties (Manaster)
- Usually occurs early in convalescence
- Patients must avoid hip flexion greater than 90 degrees (shoes and socks must
be put on with adaptive equipment, and any hip adduction (no crossing of legs).
Etiology
- Inadequate adjustment of soft tissue tension at time of surgery leading to
instability
- Loss of abductor mechanism, usually due to detachment of the greater
trochanter
- Shortening of limb with short femoral neck and high acetabular component
- Malpositioned prosthetic components
- Optimal acetabular component positioning
- Anteversion 15 +/- 10 degrees
- Lateral inclination 40 +/- 10 degrees.
- Malpositioned acetabular component
- Steep lateral inclination is associated with superior dislocation
- Retroverted cup is associated with posterior dislocation (Coventry)
- Anteverted cup is associated with anterior dislocation (Lewinnek)
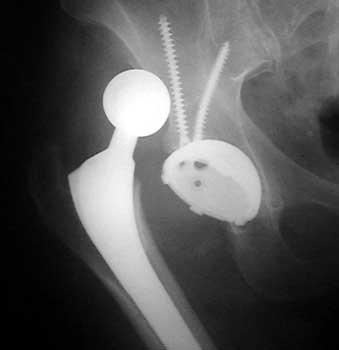
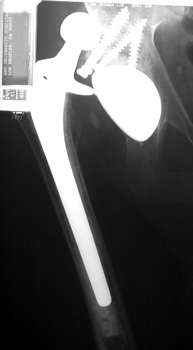
Dislocated total hip replacement
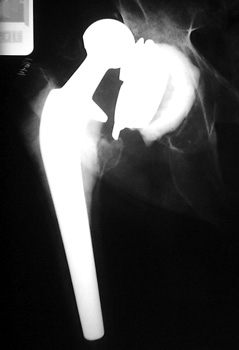
Dislocated femoral component secondary to loose acetabular cup
with reverse acetabular inclination
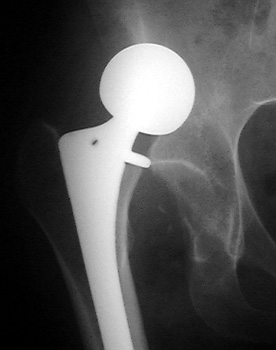 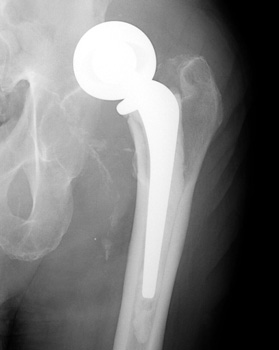
Dislocated bipolar hemiarthroplasties in 2 different patients.
 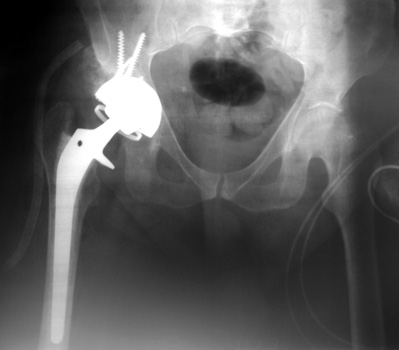
Dislocated femoral component secondary to steep acetabular cup
inclination, pre and post revision. Note constraining ring about femoral head,
which helps maintain head in cup
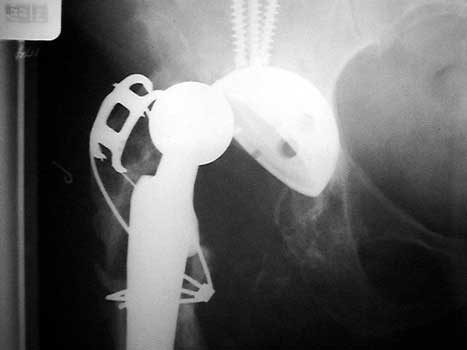 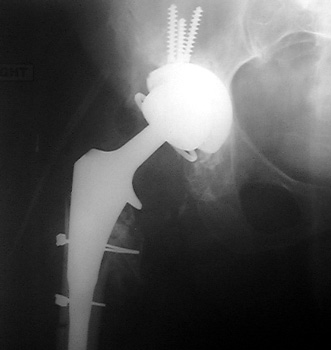
Dislocated femoral component related to non union of greater
trochanteric osteotomy. Post operative radiograph with constraining ring about
femoral head, which helps maintain head in cup. Greater trochanter resected.
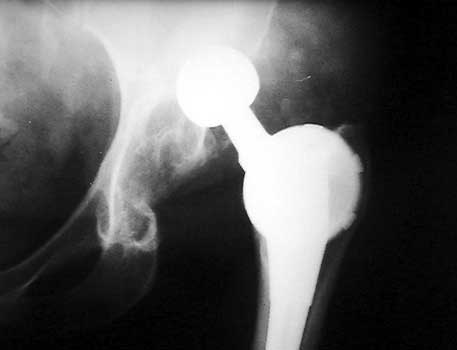
Dislocated acetabular cup and femoral component
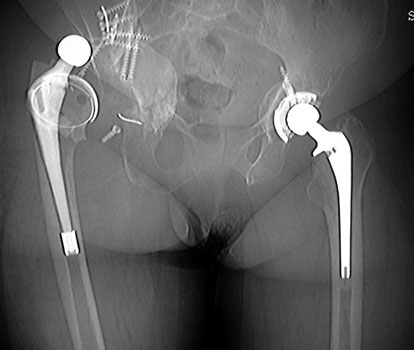 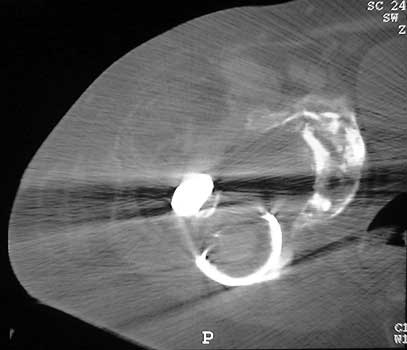
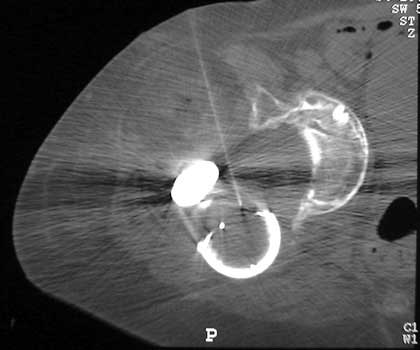
Dislocated femoral component and acetabular cup in grossly
loose arthroplasty. CT guided aspiration to rule out infection.
|