 Septic
arthritis is an infection of one of the joints which can quickly lead to joint
destruction if left untreated.
Septic
arthritis is an infection of one of the joints which can quickly lead to joint
destruction if left untreated.
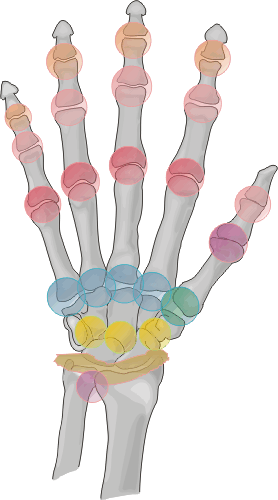
Distribution:
Involvement may mono- or poly-articular. Contamination of the joint can occur
by several mechanisms including hematogenous or contiguous spread, and postoperative
infectious. Direct implantation of organisms can also occur from a hand injury
during a brawl, or penetration from a nail, knife, etc. The metacarpophalangeal
joints are key target sites of involvement during fist fights.
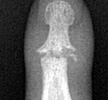
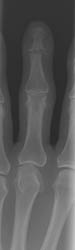
Radiographic Appearance:
Early findings include soft tissue swelling and effusions. With progression
of the infectious process, destruction of articular cartilage and bone can
lead to radiographic findings of poorly defined articular erosions and joint
space narrowing. Juxtaarticular osteoporosis and central erosions can also
be noted and ankylosis of the joint may eventually result in the most severe
cases.
Differential Diagnosis:
Although other disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or PVNS may be the
actual underlying cause, an infectious etiology must be considered when the
radiographic findings of a mono-articular destructive process are present.
Superimposed septic arthritis on a chronic arthropathy such as rheumatoid
arthritis may be difficult to differentiate from the preexisting articular
disorder.